Convert Micrograms To Iu Vitamin D
Vitamin D: A Rapid Review
Dosage of Vitamin D Needed To Achieve 35 to 40 ng/ml (90-100 nmol/L)
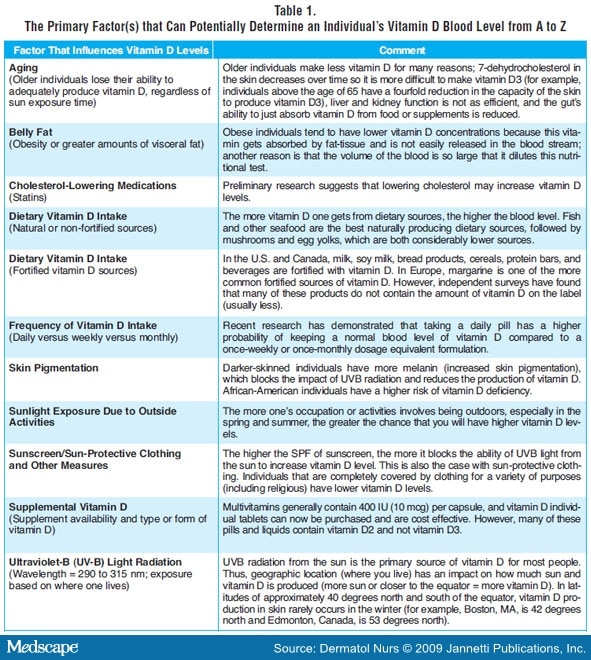
Historically, 400 IU (10 ug) of vitamin D was recommended for better health because it closely approximated the amount of vitamin D in a teaspoonful of cod liver oil. However, 800 to 1,000 IU is the dose that may have a better chance of giving a patient a normal vitamin D level. In some countries, vitamin D is listed in micrograms, and the relationship is as follows:
-
2.5 mcg (micrograms) = 100 IU.
-
5 mcg = 200 IU.
-
10 mcg = 400 IU.
-
15 mcg = 600 IU.
-
20 mcg = 800 IU.
It is much easier to access the patient's need after a vitamin D blood test. Few individuals would allow their clinician to simply guess an individual's cholesterol level before placing him/her on some type of medication. Clinicians have access to an accurate lipid test that provides guidance. The same is true for vitamin D levels. Clinicians should not suggest high intakes of vitamin D (5,000 IU for example) before recommending the 25-OH vitamin D test.
Health care professionals need to keep in mind that in general, 100 IU (2.5 mcg) of vitamin D per day can raise the vitamin D blood test only 1 ng/ml or just 2.5 nmol/L after 2 to 3 months. How much vitamin D is needed per day to obtain a normal vitamin D blood level? The following examples include:
-
100 IU (2.5 mcg) per day increases vitamin D blood levels 1 ng/ml (2.5 nmol/L).
-
200 IU (5 mcg) per day increases vitamin D blood levels 2 ng/ml (5 nmol/L).
-
400 IU (10 mcg) per day increases vitamin D blood levels 4 ng/ml (10 nmol/L).
-
500 IU (12.5 mcg) per day increases vitamin D blood levels 5 ng/ml (12.5 nmol/L).
-
800 IU (20 mcg) per day increases vitamin D blood levels 8 ng/ml (20 nmol/L).
-
1000 IU (25 mcg) per day increases vitamin D blood levels 10 ng/ml (25 nmol/L).
-
2000 IU (50 mcg) per day increases vitamin D blood levels 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/L).
If the vitamin D blood test was 30 ng/ml (75 nmol/L) and a 40 ng/ml (100 nmol/L) level was desired, 1,000 IU (25 mcg) of vitamin D per day over several months should be taken to achieve a normal blood level or 40 ng/ml (100 nmol/L). Upon reaching the goal, most individuals need to supplement with 800 to 1,000 IU per day to maintain this level. Only working closely with a clinician over time can provide the most accurate answer. However, issues of insurance and health care access suggest that 800 to 1,000 IU is ample for many individuals who are not able to have their blood tested.
Dermatology Nursing. 2009;21(1) © 2009 Jannetti Publications, Inc.
Cite this: Vitamin D: A Rapid Review -Medscape - Jan 01, 2009.
- Abstract and Introduction
- Why Most People Are Vitamin D Deficient
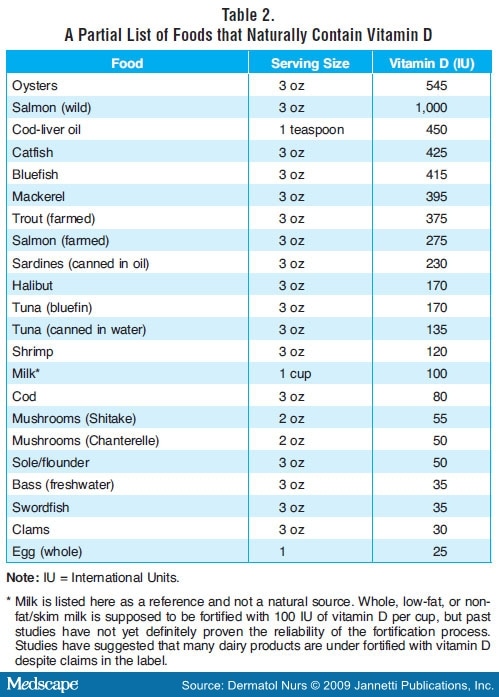
- Dietary Sources of Vitamin D
- Vitamin D2 and/or Vitamin D3
- The Vitamin D Blood Test (25-OH Vitamin D): Who, How, When, and Where
- Personal Belief Regarding Vitamin D Testing
- The "Ideal" Vitamin D Blood Level
- Dosage of Vitamin D Needed To Achieve 35 to 40 ng/ml (90-100 nmol/L)
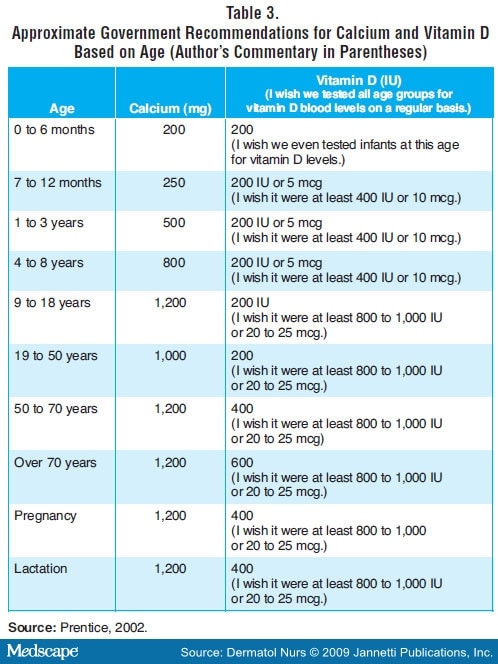
- Calcium and Vitamin D Recommended Daily Allowances
- Side Effects and Toxicity
- Conclusion
- References
Convert Micrograms To Iu Vitamin D
Source: https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/589256_8







Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar